What is Zero Trust Framework
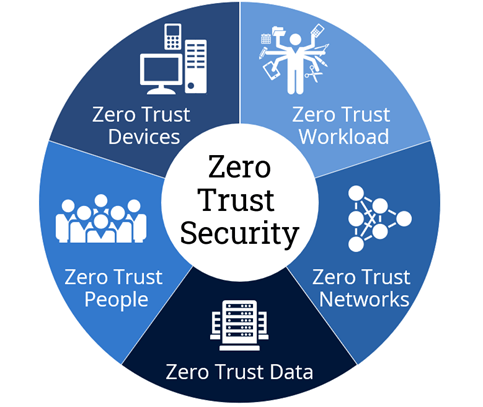
The Zero Trust Framework is a cybersecurity strategy and architectural model that challenges the traditional security approach, which typically assumes that everything inside an organization’s network can be trusted. In a Zero Trust model, trust is never assumed, and strict access controls are enforced regardless of whether a user is inside or outside the corporate network. The core principle is to “never trust, always verify.”
Key principles of the Zero Trust Framework include:
- Verify Identity:
- Authentication is a fundamental aspect. Users and devices must verify their identities through multiple factors (multi-factor authentication) before gaining access.
- Least Privilege Access:
- Users and devices are granted the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. Access is based on the principle of least privilege to limit potential damage in case of a security breach.
- Micro-Segmentation:
- Network segmentation is implemented at a granular level, dividing the network into smaller segments. This limits lateral movement for attackers, preventing them from easily accessing sensitive areas.
- Continuous Monitoring:
- Continuous monitoring of user and device behavior is essential. Anomalies and suspicious activities are promptly detected and addressed.
- Device Health Verification:
- The security posture of devices (such as computers, smartphones, and IoT devices) is continuously assessed to ensure they meet security standards before granting access.
- Encryption:
- Encrypted communication is encouraged, especially for data in transit. This safeguards sensitive information from interception.
- Strict Access Controls:
- Access controls are strictly enforced based on user roles, responsibilities, and contextual information. Dynamic access policies may change based on the user’s location, device status, or other contextual factors.
- Continuous Authentication:
- Rather than a one-time authentication at login, the Zero Trust model promotes continuous authentication. Users are required to re-authenticate during their session based on various factors.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA):
- UEBA tools are employed to analyze patterns of behavior among users and entities. Deviations from normal behavior can trigger alerts for further investigation.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE):
- SASE combines network security functions with WAN capabilities to support the dynamic, secure access needs of organizations. It aligns with the principles of Zero Trust by providing security services close to the user or device.
The Zero Trust Framework is particularly relevant in the current cybersecurity landscape, where traditional perimeter-based security models are considered insufficient due to the rise of remote work, cloud computing, and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. By adopting a Zero Trust approach, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and better protect against internal and external threats.